Table of Contents
Executive Summary
A Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy is a crucial plan that outlines how a company will sell its products or services to its target market. This article provides an in-depth overview of GTM strategies, including key components, methodologies, and best practices to ensure successful market entry and sustainable growth. By aligning resources, marketing efforts, and sales activities, a well-crafted GTM strategy helps businesses achieve competitive differentiation, customer acquisition, and increased revenue.
Introduction
In today’s dynamic and competitive business landscape, having a clear and structured GTM strategy is essential for any business seeking to optimize its market presence. Whether launching a new product or entering a new market, a solid GTM strategy ensures that a company understands its target audience, competition, and the value proposition it delivers. This article explores the significance of a GTM strategy and how it serves as a roadmap for businesses to successfully position their offerings.
Understanding Go-To-Market Strategies
Definition
A Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy is a tactical plan outlining how a company will introduce a product or service to the market and reach target customers while gaining a competitive edge. It encompasses critical elements like market research, product positioning, sales strategy, marketing plans, and optimal distribution channels. A well-defined GTM strategy aligns all departments, such as product, sales, marketing, and customer success, toward a common goal, detailing how the company will differentiate itself, communicate its unique value proposition, and foster strong customer relationships.
Importance
A well-defined GTM strategy is crucial for several reasons, as it ensures that all facets of market entry and growth are strategically planned and executed. Some key reasons for its importance include:
- Market Alignment: A GTM strategy ensures that the product or service is fully aligned with the needs and preferences of the target market. Through thorough market research and segmentation, businesses can identify the right customer base and tailor their offerings accordingly. This alignment between the product and market needs significantly enhances the chances of customer adoption and long-term success.
- Resource Allocation: One of the primary functions of a GTM strategy is to optimize the allocation of resources, particularly in marketing and sales. With a clear understanding of the target market, customer segments, and channels, businesses can invest resources more efficiently, focusing on the activities and channels that offer the highest return on investment.
- Risk Mitigation: Launching a new product or entering a new market is fraught with risks, including market uncertainty, competition, and customer resistance. A GTM strategy helps identify potential risks early on, such as unmet customer needs, incorrect pricing models, or poorly chosen distribution channels. By pinpointing these challenges, businesses can develop mitigation strategies, such as pivoting their positioning, revising pricing, or adjusting marketing tactics before they lead to larger setbacks.
Key Components of a GTM Strategy
A Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy requires careful planning and alignment across several key components to ensure success. Each of these elements plays a vital role in helping businesses understand their market, connect with customers, and drive growth. Below is a detailed breakdown of the critical components of a successful GTM strategy.
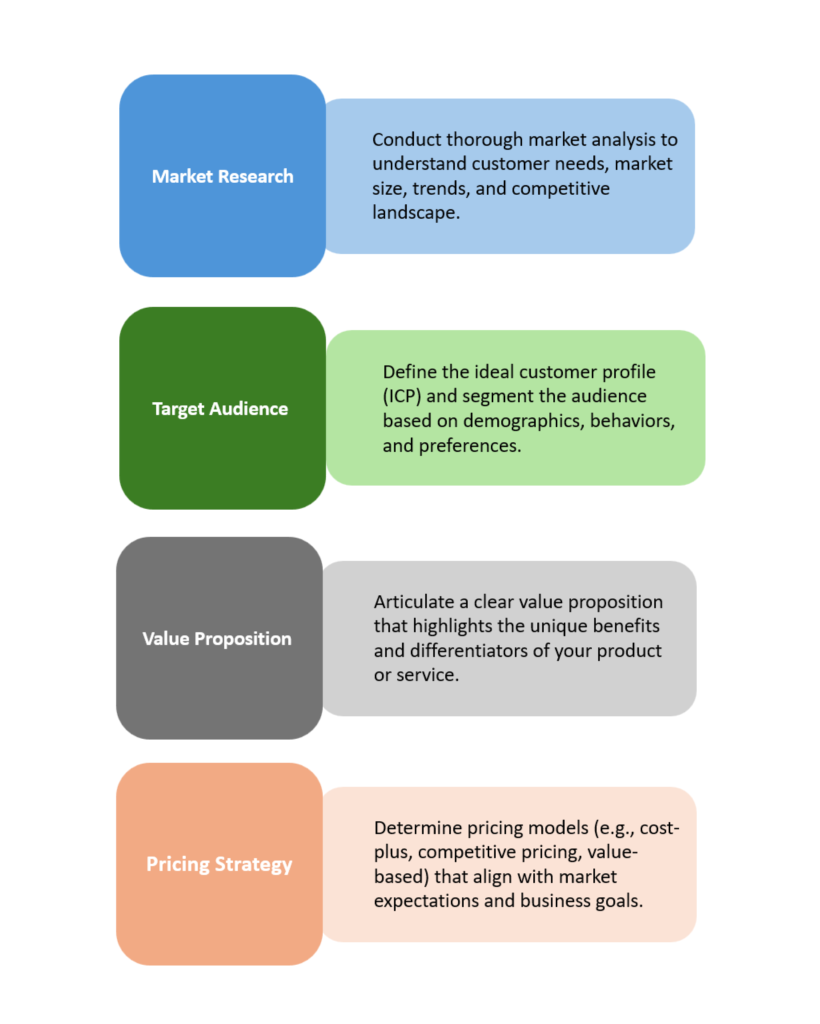
- Market Research: Market research is fundamental to any GTM strategy, providing insights into customer needs, market size, trends, and competitors. It combines qualitative and quantitative data from surveys, focus groups, and industry reports, helping businesses answer key questions about competitors, unmet customer needs, and market evolution. Skipping this step risks market misalignment.
- Target Audience: Defining the target audience ensures focused marketing and sales efforts. Creating an Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) details the characteristics of customers who benefit most from the product. Audience segmentation based on behaviours and preferences allows for tailored messaging, enhancing relevance for different customer groups.
- Value Proposition: A strong value proposition differentiates a product by articulating its unique benefits and addressing customer pain points. It should highlight features that solve problems, showcase measurable outcomes, and emphasize innovations. A compelling value proposition builds brand identity and guides marketing messages.
- Pricing Strategy: The pricing strategy influences customer perception and market competitiveness. It should reflect product value while aligning with market expectations and profitability. Common models include cost-plus, competitive, value-based, and penetration pricing. Pricing should remain flexible to adapt to market conditions.
- Distribution Channels: Selecting the right distribution channels ensures effective product reach. Options include direct sales, online channels, retail distribution, and partnerships. An effective strategy considers where target customers are most likely to discover and purchase the product.
- Marketing Strategy: An integrated marketing strategy builds demand and brand awareness through multi-channel tactics. Key tactics include content marketing, social media, email campaigns, and paid advertising. The strategy should allow for ongoing optimization based on performance data and customer feedback.
- Sales Strategy: A clear sales strategy defines how the sales team engages with prospects and maintains customer relationships. It includes sales tactics, training, tools, and forecasting. Collaboration between marketing and sales ensures aligned messaging and efficient customer acquisition.
- Measurement and KPIs: Setting metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial for tracking the success of the GTM strategy. Key KPIs include Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), conversion rates, market share growth, and Return on Investment (ROI). Regular KPI reviews help optimize performance and drive continuous improvement.

7 Easy Steps to Formulate an Effective Go-To-Market (GTM) Strategy
What are Your Target Markets?
Identifying the right target markets is the first step in any GTM strategy. Conduct comprehensive research on demographics, customer behaviour, and the competitive landscape to prioritize markets that align with your goals. Focus on those with growth potential and unmet needs to maximize the chances of success.
Who are Your Target Consumers?
Create detailed customer profiles based on characteristics like age, lifestyle, and purchasing behaviour. Use surveys and market research to gain insights into their needs and preferences, which will help you tailor your messaging and offerings to address their specific pain points.
What about Branding and Positioning?
Branding and positioning define how your product is perceived in the marketplace. Develop a clear unique value proposition (UVP) that sets you apart from competitors. Consistent messaging and a strong brand identity will help build loyalty and trust among your target audience.
What are You Offering?
Outline your product’s key features and benefits, ensuring they meet the needs of your target customers. Highlight what makes your product unique, whether it’s innovative technology, superior quality, or better customer service, and communicate that clearly to potential buyers.
What are Your Channels?
Determine the most effective channels, both online and offline, to reach your audience. Analyze where your customers prefer to engage, whether it’s through e-commerce, social media, retail stores, or direct sales, and optimize your strategy to match those preferences.
How Will You Build Your Budget Model?
Develop a budget that accounts for all aspects of the GTM strategy, including marketing, sales, operations, and distribution costs. Allocate resources strategically to ensure sustainable growth while avoiding overspending in areas that may not provide immediate returns.
What is Your Marketing Strategy?
Craft a marketing plan that includes clear messaging and promotional tactics across multiple channels such as content marketing, social media, paid ads, and PR. Set measurable goals and KPIs to track performance and make data-driven adjustments to optimize your strategy over time.
By following these steps, businesses can create a targeted, efficient GTM strategy that maximizes their chances of success in the market

Methodologies for Developing GTM Strategies
- Lean Startup: The Lean Startup methodology emphasizes rapid, iterative development with constant customer feedback. By launching a minimum viable product (MVP) and refining it based on real-world user insights, businesses minimize wasted resources. This approach ensures that offerings are continuously adjusted to meet evolving market needs, reducing the risk of misalignment.
- Agile GTM: Agile Go-To-Market strategies focus on continuous improvement and quick iterations, allowing companies to rapidly adapt to market changes, consumer behaviour or competitive pressures. It encourages collaboration across teams and quick pivots in response to feedback, making it ideal for fast-paced industries.
- Product-Market Fit: Achieving product-market fit ensures that a product addresses a significant problem for its target audience. Testing in real-world environments confirms that the product resonates with customers, leading to higher satisfaction, reduced churn, and stronger market traction.
Best Practices for GTM Execution
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: A successful GTM strategy relies on teamwork between marketing, sales, product development, and customer support. Each team’s unique insights contribute to a cohesive strategy that enhances product positioning, messaging, and customer acquisition. Regular communication helps identify and resolve issues early.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Keeping customers at the center of the GTM strategy is key. Engaging them through surveys, interviews, and pilot programs offers insights into their needs and preferences. Incorporating feedback ensures the product and messaging stay relevant, building loyalty and stronger relationships.
- Pilot Programs: Testing a product in specific regions or through pilot programs before a full-scale launch helps gather feedback, identify issues, and make adjustments. This incremental approach reduces risk and increases the likelihood of a successful launch.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Using analytics tools to track marketing, sales, and customer engagement allows businesses to make informed decisions. Monitoring key metrics like conversion rates and customer lifetime value helps refine strategies and stay competitive.
Challenges in GTM Strategy Implementation
- Market Misalignment: One common GTM challenge is failing to align the product with market needs. Companies often misjudge customer demand, underestimate competition, or misposition their product due to insufficient research, leading to poor product-market fit and hindered success.
- Resource Constraints: Many companies, especially startups, face budget and personnel limitations, making it difficult to execute a comprehensive GTM strategy. Lack of resources for marketing, development, and customer support can create gaps that impact market success.
- Competition: In competitive markets, standing out can be tough. Competitors often have bigger budgets, brand recognition, and established customer bases. Differentiation, innovation, and agility are key to navigating this landscape effectively.
Conclusion
A robust Go-To-Market strategy is critical for any company looking to achieve sustainable growth and gain a competitive edge. By understanding and implementing key components such as customer research, pricing models, and distribution channels, businesses can successfully navigate the complexities of market entry. Additionally, leveraging methodologies like Lean Startup and Agile GTM helps to maintain flexibility, while best practices such as cross-functional collaboration and data-driven decisions ensure continuous refinement of the strategy. Despite the challenges that may arise, companies that focus on achieving product-market fit, listening to customers, and maintaining an agile mindset are more likely to succeed in the long run.








