Table of Contents
Generative AI has evolved far beyond just text prompts. Users can now interact through voice, sketches, and images often within a single session. Multi-modal AI offers versatile experiences, but designing for it requires context-awareness, clarity, and intuitive interaction. Successful UX ensures users accomplish tasks efficiently while mapping it with how the AI interprets users’ inputs.
1. Offering Flexible Input Options
Users expect the freedom to switch between input modes in the same interface, but presenting all options at once can be extremely overwhelming.
- Google Lens demonstrates effective flexibility. The users can take a photo, highlight a section, and refine the search with text. Tools appear contextually, guiding users and helps avoid overwhelm and confusion.
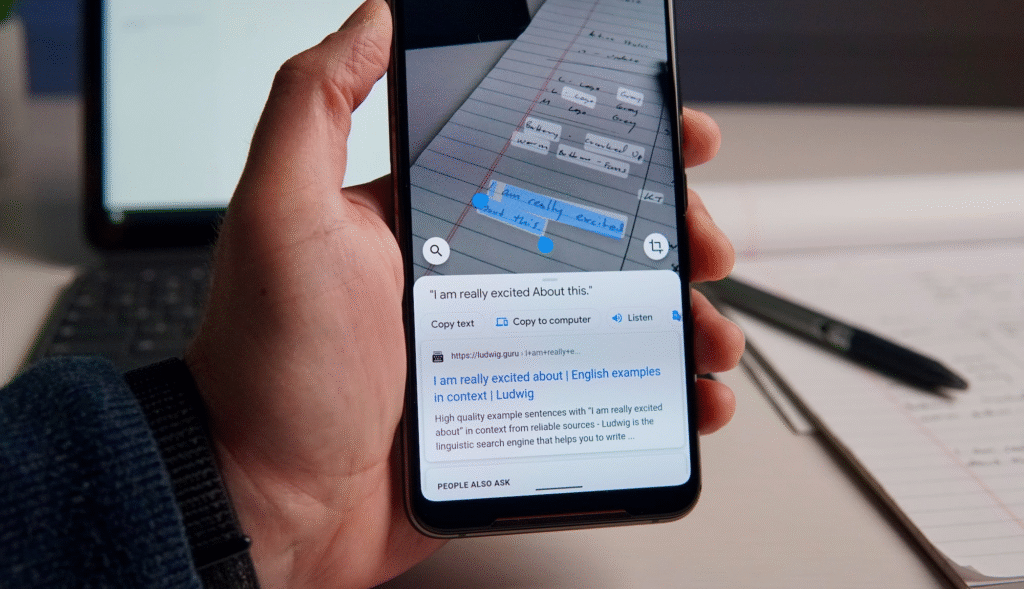
- Effective UX design should group input modes logically, use crystal clear visual cues, and reveal advanced options in a progressive fashion. This allows users to explore capabilities of the interface at their own pace without cognitive overload.
2. Preserving Context Across Input Modes
Switching between text, voice, or images shouldn’t disrupt ongoing tasks or the existing flows. Maintaining seamless mode switching is critical for trust and usability.
- In the ChatGPT mobile application, the users can dictate a question and then refine the response via text typing without losing conversation context.
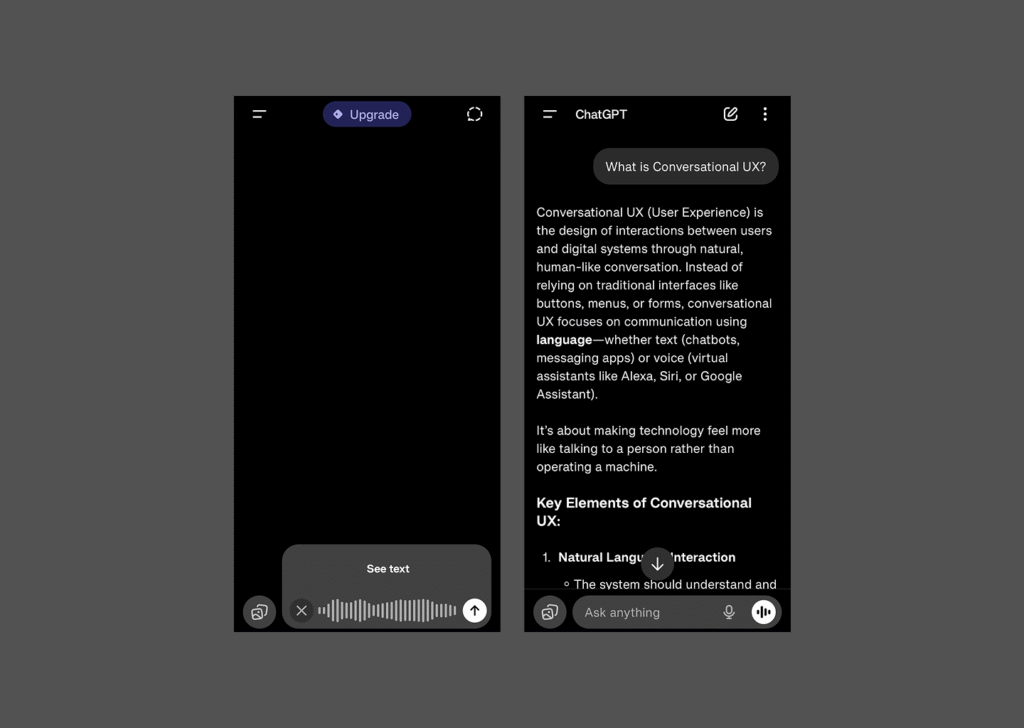
- Effective UX requires invisible state management, so each input contributes to the same workflow and outcomes instead of creating fragmented sessions.
3. Reducing Friction from AI Misinterpretation
AI outputs can sometimes misinterpret user input or can hallucinate. Designing UX for Gen AI interfaces should anticipate errors and provide clear recovery paths.
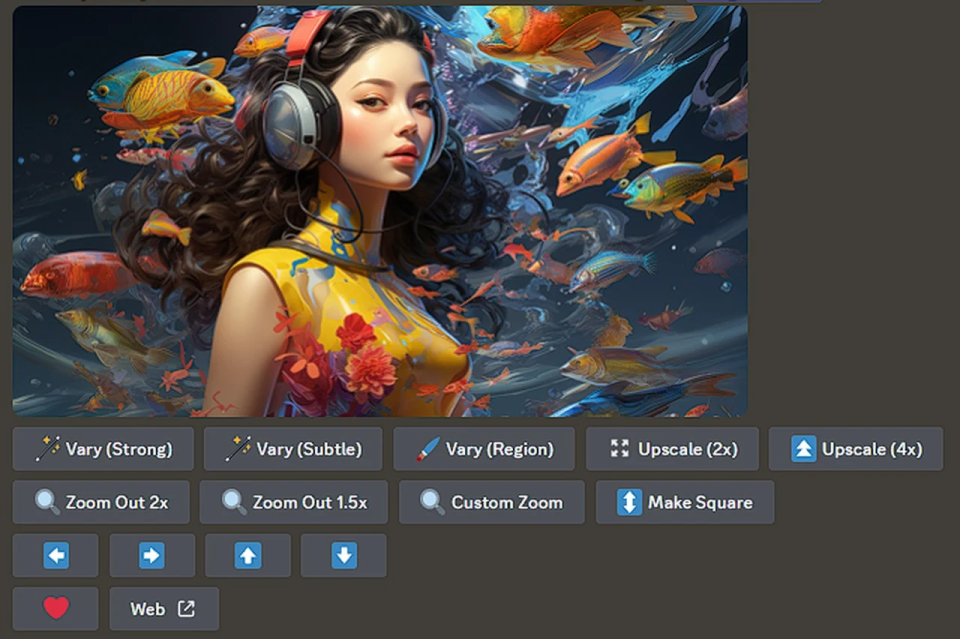
- MidJourney allows users to generate more variations, upscale, or redo images when outputs aren’t as expected, turning potential frustration into exploration and correction.
- Visual recognition apps often highlight detected objects, helping the users understand how the AI interpreted the input and enabling quick corrections for improved task completion and user satisfaction.
4. Making AI Decisions Transparent and Feedback Oriented
Users trust AI interfaces more when they understand their reasoning. Transparent feedback communicates AI interpretation without overwhelming the user.
- Pinterest Lens highlights the specific image area influencing the recommendations.
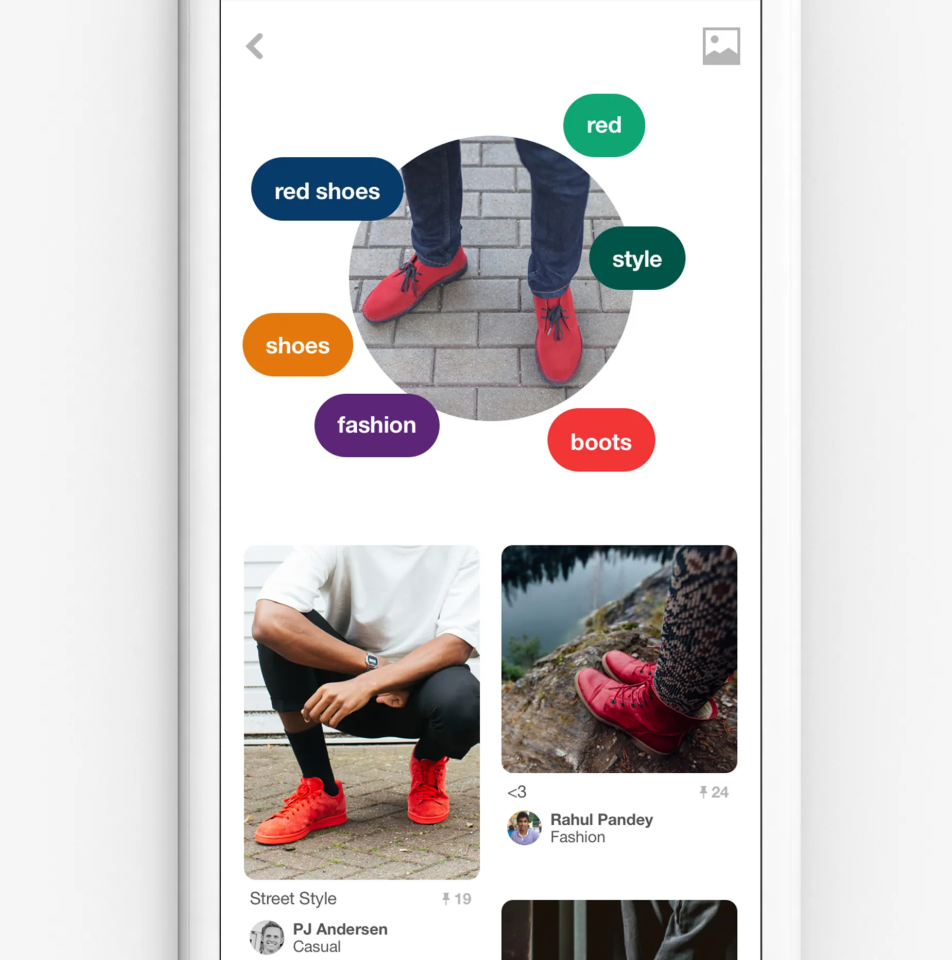
- Voice-enabled AI tools display the transcripts alongside generated results, ensuring users see exactly what the AI has captured.
- Well-designed interfaces surface AI understanding visually or textually, increasing confidence while reducing error rates.
5. Designing for Accessibility and Inclusivity
Multi-modal AI provides opportunities to make technology accessible to a wide range of users, but only with deliberate design.
- Microsoft Seeing AI enables visually impaired users to point a camera at an object and receive audio descriptions in real time.
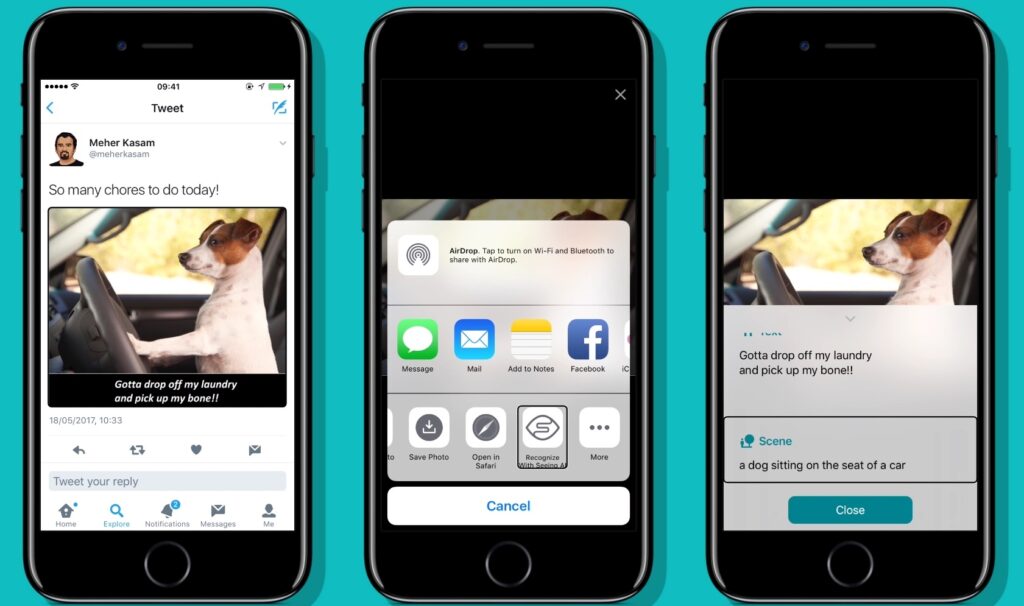
- Voice input in Google Lens enables users with limited mobility or typing ability to interact efficiently.
- AI Interfaces should ensure all modes complement each other, while outputs remain clear, readable, and usable cross-platform.
6. Integrating Multiple Modes Seamlessly
Real-world interactions rarely rely on a single mode. Users naturally combine modes to complete tasks faster.
- A student may upload a photo of a math problem and then type a clarifying or a follow up question. The AI must maintain context, interpret both inputs, and provide the relevant results. AI tools should be designed with such capabilities.
- Designers using Notion AI can upload images and add textual instructions simultaneously for refining the content.
7. Supporting Natural Interaction Patterns
Effective multi-modal UX aligns with real user behavior such as the following:
- Task-driven switching: Users often start with one mode and follow up with another as needed to get the desired output and fine tune it.
- Error mitigation: Highlight AI interpretations and provide quick correction paths to reduce frustration and improve task completion.
- Combined input enhancement: Multiple inputs should work in tandem to improve accuracy and usefulness.
Conclusion
These patterns allow users to focus on goals, avoids complexity, and make interactions predictable and productive. Generative AI is advancing rapidly, but UX remains the differentiator between frustrating and delightful experiences. If executed well, multi-modal AI doesn’t feel complex. Users seamlessly switch modes and complete tasks efficiently and confidently.